These sodium channel blocking drugs are used to test for Brugada syndrome in patients suspected of Brugada syndrome but without a spontaneous type-1 Brugada ECG (see below). Tests should always be performed under continuous ECG monitoring and controlled conditions (see also Antzelevitch 2005). Drug administration during the tests differs per drug used but regularly the drug is administred in 5 to 10 minutes either continuously or in 1 minute intervals (see table below) untill a diagnostic ECG, arrhythmias, excessive conduction abnormalities or maximal dose are reached. Post-test monitoring depends on the half life of the chosen drug (ajmaline several minutes, flecainide 20 hours, procainamide 3-4 hours), and is recommended untill the ECG has returned to baseline conditions. To diagnose Brugada syndrome instead of solely a Brugada ECG, there are several other criteria which should be met (see the consensus reports: Wilde 2002, Antzelevitch 2005 and Priori 2013,)
Notes about the lists:
- On this list we summarized the drugs that are generally regarded in the literature as appropriate to perform a diagnostic test for Brugada syndrome. Please note that these drugs (most probably) have a lower than 100% sensitivity and specificity for Brugada syndrome (Priori 2000). In addition there is difference between these drugs where sensitivity and specificity are concerned (e.g. flecainide seems to have considerable lower sensitivity than ajmaline).
- Drugs are listed with up to 2 common brand names. There are several brand names for many of the drugs, which are not all listed. It is also important to look at the active drugs in medicines that contain a combination of drugs.
- Lists contain links to DrugBank or PubChem (click on the drug name) and also (several) PubMed links to articles on the association between the drug and Brugada syndrome (click on the reference).
Please also read our Disclaimer.
| Generic name | Brand name® | Clinical use | Comments / References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ajmaline | e.g. Gilurytmal® | Antiarrhythmic Agent (1A) / Arrhythmias | Used for diagnostic test (maximal dose 1mg/kg, infused continuously over 5 minutes or in boluses 10mg/min) Brugada 1997 Rolf 2003 Wolpert 2005 |
| Flecainide* | e.g. Tambocor® | Antiarrhythmic Agent (1C) / Arrhythmias | Used for diagnostic test (maximal dose 2mg/kg or 150mg, either continuously over 10 minutes or in boluses of 10mg/min) Krishnan 1998 Brugada 2000 Gasparini 2003 Wolpert 2005* Meregalli 2006 |
| Pilsicainide | e.g. Sunrhythm® | Antiarrhythmic Agent (1C) / Arrhythmias | Used for diagnostic test (maximal dose 1mg/kg, administration equal to ajmaline) Takenaka 1999 Fujiki 1999 Takagi 2002 |
| Procainamide# | e.g. Procan® Pronestyl® | Antiarrhythmic Agent (1A) / Arrhythmias | Used for diagnostic test (maximal dose 10mg/kg, either continuously over 5 to 10 minutes or in boluses of 100mg/min) Miyazaki 1996 Brugada 1997 Joshi 2007 |
* It has been reported by Wolpert that flecainide has a 32% lower sensitivity to uncover a type-1 Brugada ECG than ajmaline.
# In the first consensus report (Wilde), the sensitivity of procainamide was considered relatively low.
The diagnosis of the characteristic type-1 (or coved type) Brugada ECG (figure 1) is made from the right precordial ECG leads (see also Wilde 2002). Sensitivity of the ECG can be increased with alternative placement of ECG leads to the intercostal space above V1 and V2 (figure 2).
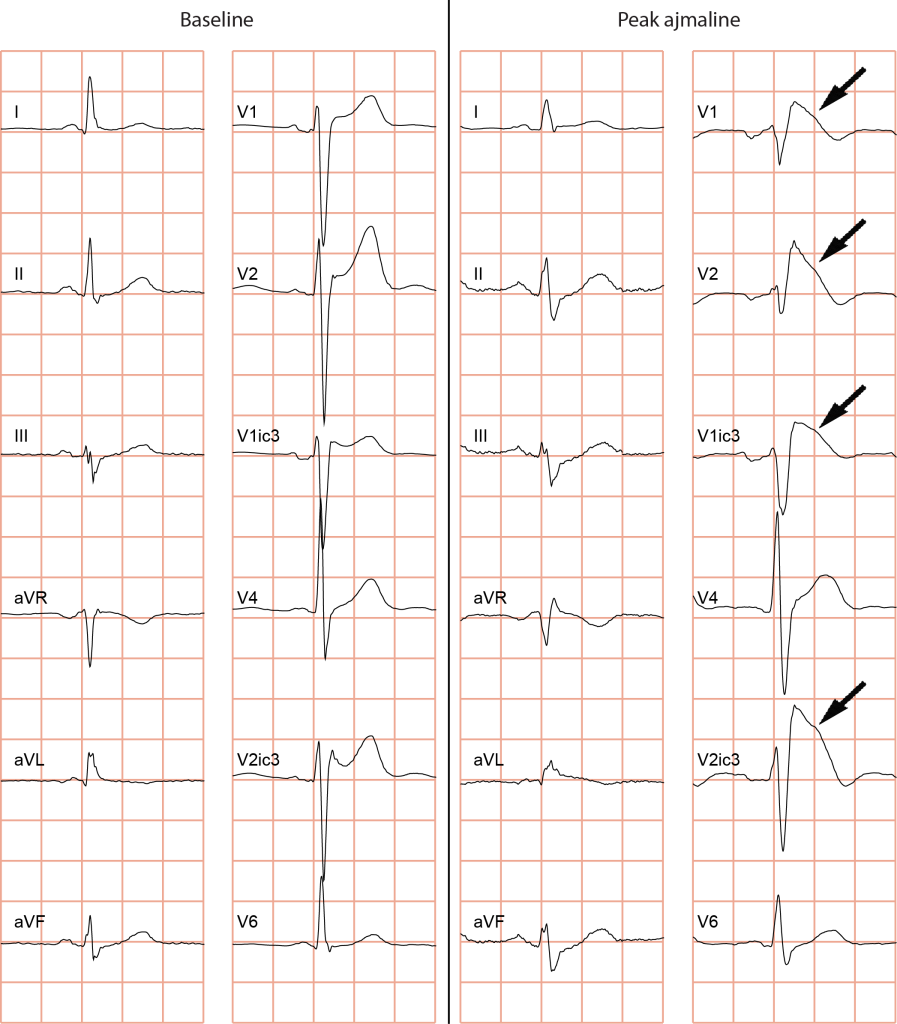 |
| Figure 1: Change of a normal ECG into a type-1 Brugada ECG during ajmaline challenge. Note the coved type ST segments in the right precordial ECG leads (note V3 is placed in the 3rd intercostal space above V1 [V1ic3], and V5 is placed in the 3rd intercostal space above V2 [V2ic3]). For more ECGs, see ECGpedia.org. |
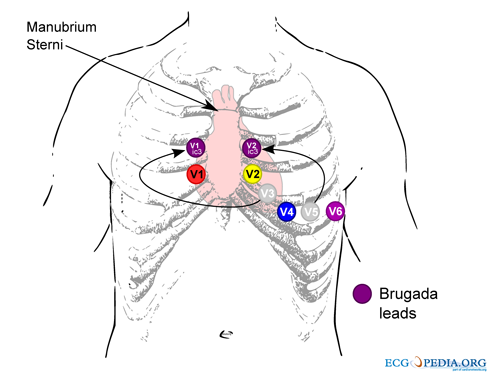 |
| Figure 2: Alternative ECG lead placement for Brugada syndrome. Figure from ECGpedia.org |
Disclaimer and Waiver
The information presented is intended solely for the purpose of providing general information about health related matters. We do our best to ascertain that all information on this site is correct and up-to-date. However, we cannot guarantee that it is. The information provided here is for educational and informational purposes only and designed primarily for use by qualified physicians and other medical professionals. It is not intended for any other purpose, including, but not limited to, medical or pharmaceutical advice and/or treatment, nor is it intended to substitute for the users’ relationships with their own health care/pharmaceutical providers. To that extent, by continued use of this program, the user affirms the understanding of the purpose and releases the Academic Medical Center, the BrugadaDrugs.org Advisory Board and Cardionetworks from any claims arising out of his/her use of the website.